








جمعية تكنولوجيا الهندسة الطبية
24/03/2022
3D printing is a manufacturing technique commonly known as additive manufacturing; it is based on the principle of layered manufacturing, in which materials are overlapped layer by layer to construct any desired object.The common materials utilized for 3D printing are polymers and metals. The main porpuse of 3D printing is to enhance the earliest stages of product development by quickly and easily made prototypes at an optimum cost. 3D printing has been widely utilized in various aspects of our lives and in many areas, such as:
Engineering Prototypes-
Education-
Medical and Dental sector-
Aerospace-
Automobiles-
Construction-
Art and Jewelry-
Consumer goods-
3D Printing Applications in medical filed, 3D printing can be categorized in the following categories: tissue and organ fabrication, prosthetic, implants, anatomical models, drug delivery, and dosage forms.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
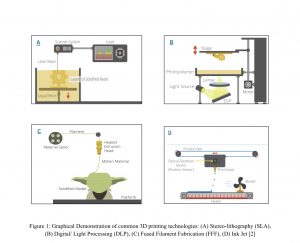
-Stereo-lithography (SLA)
-Digital Light Processing (DLP)
-Fused Depostion Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
-InkJet
-PolyJet
-Direct Metal Laser (DML)
-Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
-Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
-Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
Stereo-lithography (SLA)
An SLA process uses photopolymers (liquid plastic), a laser, and a platform inside a vat. Photopolymers are used to form a solid in a very precise manner. The laser is used to react with the resins and shape them. The photopolymer resin is held inside a vat by a removable platform. A laser beam is directed in X-Y axes across the surface of the resin, hardening it exactly where the beam hits that surface, as per the 3D data inserted into the printer. After the first layer is finished, the platform within the vat declines by a certain ratio in the Z axis, and the laser starts tracing the next layer. The process is repeated until the entire desired object has been completed and the platform has been removed from the vat.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Similar to SL, DLP is a process that utilizes photopolymers, however, the light source differs. A conventional light source such as an arc lamp, accompanied with a mirror or lens are used in DLP, accelerating the process.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
FFF is the most common process used which can be found in many offices and studios. The highlight of this process is the filament and the nozzle. The material used is a thermoplastic in the shape of a string called filament, which is extruded in a heated orifice called nozzle. The heated material is then deposited in a platform layer by layer until it cools down resulting a final product.
Ink Jet: Material Jetting
Material jetting is analogous to inkjet printer, the difference is the material used for printing, which is a photopolymer. Material jetting forms many layers by drops of photopolymer; each successive layer is shaped and dried using ultraviolet light (UV).
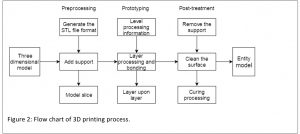
3D Printing Process steps
The process of 3D printing includes four steps, establishing of 3D model, preprocessing, prototyping, and post-treatments as shown in the Figure 5
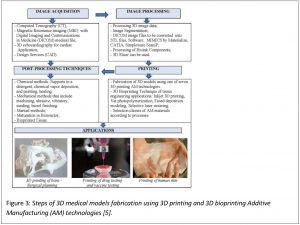
3D Printing Process steps for medical application
In medical filed, 3D printing is based on 4 steps: (1) Image Acquisition of 3D imaging data with Computed tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), with Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) medical file format, (2) Image processing, including segmentation steps and surface modeling, (3) Manufacturing with 3D printer or 3D bioprinter and (4) Post-processing techniques, as shown in the figure [3].
As any other application, employing 3D printing has both its pros and cons compared to conventional manufacturing methods. When it comes to the limitations of 3D printing, material variety, repeatability, and size restriction are major limitations of the industry.
Disadvantages
High initial cost to acquire additive manufacturing equipment-
Materials limitation lies to the fact not all material can withstand the high temperatures of the printer-
Repeatability means that not all products produced by the printer are identical, which is due to difference in inherent cooling temperature during the process-
Size of the printed products is limited due to the size of the printing chambers, hence, anything large will be printed in separated, individual parts-
The advantage of 3D printing includes those related to design, cost and time amongst other, such as
Advantages
Flexible design more than traditional manufacturing process, 3D printing has-
Rapid prototyping that can print parts within hours-
Inexpensive tool-
Strong and Light-weight durable parts-
Fast design and production-
Environmentally friendly-
Advanced Healthcare-
Finally, the technology of 3D printing is predicted to revolutionize almost every industry and change our life-style. 3D printing's tool-less nature allows for unparalleled creative freedom while also lowering costs and fostering innovation. 3D printing is also gaining attention as an energy-efficient technique that can help the environment in two ways: during the production process, by using its standard materials, and during the product's lifetime, by making it lighter and stronger.
Resources:
[1] Redwood, B., Schöffer, F. and Garret, B., 2017. The 3D printing handbook. 1st ed. 3D Hubs.
[2] Hanaphy, P., Sertoglu, K. and Everett, H., 2022. The Free Beginner's Guide - 3D Printing Industry. [online] 3D Printing Industry. Available at: <https://3dprintingindustry.com/3d-printing-basics-free-beginners-guide#07-benefits-value> [Accessed 14 March 2022].
[3] 3D Printing. 2022. What is 3D Printing?. [online] Available at: <https://3dprinting.com/what-is-3d-printing/> [Accessed 14 March 2022].
[4] https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/faqs/what-is-3d-printing/pros-and-cons
[5] https://doisrpska.nub.rs/index.php/conterporarymaterials3-1/article/view/7987