Suction Machine
المقالات >
Suction Machine
فريق LUOBME
Description & ECRI no.
An aspirator, also known as a suction machine, is a specific type of medical device generally used to clear obstructions, such as respiratory secretions (mucus and/or saliva), vomiting, blood, or foreign substances, from the patient’s airway, including the lungs and/or windpipe. Suction machines assist in breathing by maintaining a clear airway when a person is unable to expel secretions due to unconsciousness or during ongoing medical procedures. Additionally, surgeons can use it on other parts of the body to remove blood, allowing them to view and operate during surgeries [1]. The emergency care research institute (ECRI) number for the suction machine is 15051 [2].
Leader Manufacturers
There are many companies that manufacture suction machines. The following are some of the companies that are in the market [3]:
- Nouvag.
- Medela.
- Bıçakcılar.
- Axion.
- Lamidey Noury Medical.
End User & Location
The machine is used by trained healthcare providers, including doctors, nurses, and pre-hospital providers. Moreover, patients could acquire the machine, according to their condition, after training one of their family members. [1]
The suction machine can be found in the pre-hospital settings as well as the in-hospital settings, including the following: [1]
- The emergency room (ER)
- The operation room (OR)
- The intensive care unit (ICU)
- The neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)
- The delivery room (DR)
However, certain portable suction machine types are obtained by patients at their homes [1].
Class & Type
The suction machine is classified under class II as it has a medium to high risk to the patient [4]. Based on the IEC 60601-1 standard, suction machines are typically categorized as Type B since it provides a particular degree of protection against electric shock (earth referenced) and have no direct connection to the patient. [5][6]
Design & Installation
Although the machine’s design differs among manufacturing companies, all designs consist of main parts shared by different manufacturers as the following: [7]
- Canister holder
- An outlet filter
- Pressure regulator
- Pressure display panel (gauge)
- AC plug and/ or a battery and charger
- A power switch

Figure 1. A suction machine manufactured by Medela Healthcare company. [8]
Installation
To prepare the suction machine before utilizing it, carefully examine its exterior and confirm the presence of all listed components from the manufacturer in proper condition. Additionally, conduct a thorough inspection of the following: [9]
- Connect the tubing system and the canister as illustrated in the user manual. Note that the connections between the suction machine and the pipeline should be brief and straight, thus allowing a convenient transmission to the canister.
- Connect the machine to the power source.
- Turn the vacuum regulator to the maximum and block the catheter with an object, the thumb, or bend the patient tubing in a “V” form.
- Start the suctioning and notice if there is an issue, e.g., a strange sound. The vacuum indicator should reach up to the Negative pressure in a short time. After releasing the patient tubing to its original status, the pointer will return below 0.02Mpa (the value could vary depending on each company).Eventually, this inspection will indicate the functionality of the machine. However, some suction machines are programmed to start a self-check to ensure the machine’s functionality.
Components & Principles of Operation
Though the machine could differ regarding each company, the core components are the same as listed below: [1, 8]
- Vacuum regulator knob:It controls the force of suctioning.
- Vacuum indicator:It helps the user to indicate the suctioning force.
- Suction/ vacuum pump: It is located inside the machine, as shown in figure 3, and is responsible for creating negative pressure, allowing the suctioning process occurrence.
- Power cord:The suction machine is connected to the power supply through power cords to operate and charge the batteries.
- Batteries:They can be either disposable or rechargeable. Suction machines are equipped with qualified batteries to provide portability and act as a power source in case of a steady power source absence.
- Vacuum tubing:This ties the canister and vacuum pump together. The pump must never encounter anything from the canister.
- Patient tubing:It is connected to the suctioning tip (catheter) to transfer secretions from the patient into the canister.
- Canister or collecting jar:The canister accumulates the patient’s secretions. Usually, it has overflow protection features in case of excessive fluid suctioning.
- Filter:One end is attached to the machine while the other end of the filter is attached to the canister to prevent contamination of the machine’s internal components. Moreover, specific filters can be installed to safeguard against dust and hazardous gases that could harm the equipment.
The figure below illustrates the main components of a suction machine.

Figure 2. Components of a suction machine, model super vega suction aspirator, from Gruppo Industriale Milanese Aghi ( GIMA) [8]
Principle of operation
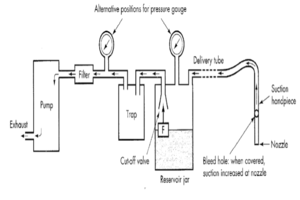
Suction machines pull and remove fluids by generating negative pressure using a Suction/vacuum pump, as shown in Figure 3. That negative pressure creates a vacuum effect that drags the secretions out of the body to the canister. The user can control the negative pressure (suctioning force) using the vacuum regulator knob.[1] Figure 4 below shows a sketch that describes the suction machine operation process.

Figure 3. Vacuum pump of a suction machine model VP35, from Eschmann. [9]

Figure 4. Suction machine principle of operation.[10]
Test Equipment & Periodic Preventive Maintenance (PPM)
It is necessary to test the suction machine daily, weekly, and every six months based on the manufacturer recommendation to ensure safety, maintain high work efficiency, and avoid device failure in case of occlusion or leakage. [11, 12] The suction machine testing procedures do not require any test equipment, as it is illustrated below:
The daily check-up: [11]
- An exterior and interior cleaning. The machine must be clear of dust, impurities, or residues by using a sterilizing
- Ensuring an appropriate installation of the fittings and accessories.
- Performing a brief visual functional inspection before using the device.
It is worth mentioning that the weekly inspection may or may not be Performed (it depends on the rules followed by the end-user regarding the use of medical equipment). However, it could be done by conducting the following [11]:
- Applying all the daily inspections.
- Replacing the cracked parts.
- Inspecting the main cables and replacing the damaged ones.
- Inspecting the battery.
- Inspecting the vacuum regulator functionality.
Battery inspection: [12]
1- Ensure the functionality of the power cord.
2- Turn on the unit from its internal DC battery instead of using the power cord.
3- Run the DC power for 15 minutes to check the battery condition. Note the following cases during running the DC power:
- If the machine functions slowly, blinks, or stops, replace the battery.
- If the machine maintains its functionality for more than 15 min, set the regulator to the required setting, turn the
device off, and reconnect the power cord to charge the device.
Vacuum inspection: [12][13]
Close the patient tube and set the vacuum regulator to the maximum vacuum setting.
- Inspect the amount that accumulates in the pump system in 3 seconds. It should be more than 300 mmHg (might differ depending on each company).
- The vacuum readings should reach the maximum value within 10 seconds. Most devices reach a maximum value of more than or equal to 500mmHg (might differ depending on each company).
- If the vacuum does not reach the maximum value, check for leakages in the system, e.g., vacuum tubes, barb connections, the cover of the canister, filters, or any other possible vacuum problems.
Note: After checking the vacuum regulator, un-occlude the patient’s tubing. If there is a leakage in the vacuum pressure, inspect the filter following the steps below: [14]
- Remove the tube from the filter.
- Turn the knob to the maximum value.
- Watch the vacuum readings.
- Replace the filter if vacuum readings are different from the values given in the table below (the range and unit could differ depending on each company).
Table 1. Acceptable vacuum readings. [14]
|
Low vacuum |
High vacuum |
Medium vacuum |
|
Vario 8 c/i – 3kPa |
Vario 18 – 10kPa |
Vario 18c/i – 10kPa |
Monthly maintenance shall be done every six months .[11] Using the device less frequently increases the importance of monthly inspections. The monthly check includes daily and weekly inspections, in addition to the instructions below, to ensure the proper performance of the device. Figure 5 illustrates the testing steps.[13]
Testing steps: [13]
Although the method of setting the test mode could differ between each company, the testing method is mostly the same, as it’s listed below:
- Once the test mode is activated, begin the first part of the test by turning the operational Knob to the maximum vacuum
- Use the thumb, block the patient tube while observing the manometer to inspect the pressure.
- Once the first part of the test is accomplished, begin the second part of the test by turning the operational Knob to the minimum vacuum value and repeat the same steps.
The results will indicate the functionality of the machine. Start a pump system test, vacuum tube test, and patient tubing inlet test in case of failure, as illustrated below: [13]

Figure 5. Suction machine test steps.[13]
Pump system test:
1- Turn the device on.
2- Remove the vacuum tube.
3- Block the outlet with the thumb.
- If there is suction pressure, then there is no failure in the system.
- If there is no or low suction pressure, check for leakages.
Vacuum tube test
1- reconnect the vacuum tube to the device and the canister.
2- Run the test mode while blocking the vacuum tube with the thumb.
- If there is suction pressure, then the tube passes the test.
- If there is no or low suction pressure, check for leakages.

Figure 6. Pump system test.[13]
Patient tubing or canister inlet test
1- Run the test mode while blocking the patient tube with the thumb (ensure the tube’s connectivity while testing).
- If there is suction pressure, then the tube passes the test.
- If there is no or low suction pressure, check for leakages.

Figure 7. Vacuum tube test.[13]

Figure 8. Patient tubing test.[13]
It is worth mentioning that the daily and weekly inspections should be conducted by the end-user while the monthly PPM is done by the biomedical engineer/ technician.
Maintenance & Common Problems
Despite regular daily and weekly inspections, as well as scheduled preventive maintenance (PPM) every six months, suction machines can still experience functionality problems and failures. Corrective maintenance (CM) is necessary to address these issues. Table 2 outlines common suction machine problems, their potential causes, and recommended solutions.
Table 2. Common suction Machine issues, possible causes, and their solutions.
| Issue | Possible cause | Solution |
| The machine is not operating. | No power | Ø Check if the power switch is on.
Ø Use a DMM (Digital Multimeter) to inspect: Ø The power cords, if so, replace them. Ø The power outlet. Use a battery to power the machine and contact an electrician for rewiring if the power is not present. Ø The battery (in case of using it as the power source), if so, replace/ recharge it.
|
| Fuse blown. | Ø Check the wires or leaks and rectify the cause. Replace the fuse. Test the power before using the machine. | |
| Electrical cable issue | Ø Use another cable to ensure the functionality of the previous one and replace it if it is damaged. | |
| Internal wiring or switch issues | Ø If possible, open the machine and replace the damaged parts or contact the service supplier company. | |
| Low fluid flow, low pressure gauge | Tube /seal / canister leaking or disconnected. | Ø Reconnect them and replace the damaged parts. Then, inspect the change in the pressure gauge reading to ensure that the problem is solved. |
| Tubing system is blocked. | Ø Inspect and clean the blocked parts. | |
| Internal or control error | Ø Contact the service supplier company. | |
| low fluid flow, high pressure gauge | A blocked filter or tube | Ø Disconnect each tube one at a time. When the airflow stops, it means the blockage has been removed. Replace the blocked filter or remove the blockage from the tube. |
| Electrical shocks | Wiring issue | Ø Inspect the source and fix/ replace the damaged part or contact the service supplier company. |
| Manual suction is jammed. | An Internal slider is stuck. | Ø Grease the machine. |
Accessories & Spare Parts
Though the spare parts could differ among companies regarding the design and purpose of the machine, there are essential spare parts each company should provide, as illustrated in the table below. Moreover, the suction machine accessories are mainly the same as its spare parts.
Table 3. suction machine accessories & spare parts with illustrating images.
| Accessories & Spare parts | |
| Canister [13]
|
 |
| Filter [13]
|
 |
| Patient tubing [13]
|
 |
| Batteries [14] | Laerdal rechargeable battery for LCSU4 Suction Units
|
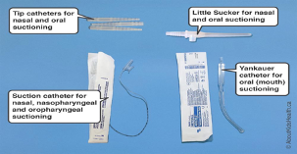
| Suctioning catheter [15]
|
A catheter is a tube attached to the patient’s tubing for suctioning purposes. There are various types of catheters depending on the suctioning method.
|
Service & Operation Manual
Service manual
The service manual is conducted by the biomedical engineer/ technician. It assists in illustrating the instructions and steps necessary to maintain and repair the medical equipment. The biomedical engineer/technician’s responsibility is to inspect the suction machine during the scheduled PPM, which is conducted every six months (the duration could differ depending on each manufacturing company). They should follow the operation manual to apply the appropriate steps to maintain the suction machine during its lifespan, as well as how to troubleshoot and repair the issues that could arise while using the equipment, as mentioned previously (under the topics: Test equipment & Periodic Preventive Maintenance (PPM) and Maintenance & Common Problems). [11,12]
Operation manual
The operation manual is used by the end-user. It assists the end-user by illustrating the instructions and steps necessary to use the medical equipment and solves its issues. The end-user should follow the steps below to operate the suction machine: [11,12]
- Turn the machine on.
- Connect the patient tubing to the suction machine.
- Connect a clean and sufficient catheter to the patient tubing.
- Lay the patient in a flat convenient position.
- Use sterile/distilled water to wet the catheter (it assists in lubricating and testing the suction machine).
- Adjust the negative pressure using the knob as regarding the doctor’s instructions.
- Carefully insert the catheter into the patient’s oropharynx in case of oropharyngeal suctioning. However, insert the catheter into the tracheostomy tube in case of tracheostomy suctioning.
- Place the thumb over the suction vent (certain catheters are designed with an opening for tracheostomy suctioning) during the suctioning process in case of applying a tracheostomy suctioning.
- Keep placing the thumb on the suction vent while removing the catheter after the suctioning. Notice that the patient can’t breathe well due to the catheter. Therefore, the catheter could only remain inside the body for a prolonged period.
- Allow the patient to recover from the suctioning for at least 10 seconds.
- Suction a small amount of distilled/sterile water with the suction catheter to clear any residual debris/secretions.
- Turn the machine off.
- Sanitize immediately after each usage.
- Discard all the connected components, including the canister, patient tubing, and catheters (in case of using disposable components, follow the proper procedures for disposing of biohazardous materials. In case of using reusable components, follow the proper procedures for cleaning and sterilizing them).
- If necessary, clean the suction machine with mild detergent and water and avoid immersing the suction unit.
References
[1]ZOLL Medical Corporation. “What is a Suction Machine?” Zoll.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.zoll.com/resources/what-is-a-suction-machine. [Accessed: Aug. 12, 2022].
[2]ECRI. “ECRI UMDNS Device Term ECRI IMDC ADG Code A Accessories, Endoscopes * ENDOAC Acupuncture Kits Adhesives Enhancers * ADHMED Adhesives,” 1998.
[3]”Surgical suction pump – All medical device manufacturers”, Medicalexpo.com, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.medicalexpo.com/medicalmanufacturer/surgical-suction-pump-3744.html.
[4]“Product Classification https://2u.pw/o9kcgePb
[5]Center for Devices and Radiological Health, “Guidance Document for Powered Suction Pump 510(k)s – Guidance for Industry and FDA Reviewers/Staff,” U.S. Food And Drug Administration, Mar. 13, 2018. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/guidance-document-powered-suction-pump-510ks-guidance-industry-and-fda-reviewersstaff
[6]“Introduction to Electrical Safety Testing: Part 2 | Fluke Biomedical.” https://a.flukebiomedical.com/Introduction_to_Electrical_Safety_Testing_-part_2
[7]AboutKidsHealth”, Aboutkidshealth.ca, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/article?contentid=3851&language=english. [Accessed: 12- Aug- 2022].
[8]“Dominant Flex and basic surgical suction pumps,” Medela, https://www.medelahealthcare.com/en-US/solutions/professional-vacuum-solutions/surgical-airway-suction/dominant-flex-and-basic-suction-pumps (accessed Apr. 27, 2024).
[9]“Portable Phlegm Suction Unit User’s Manual Please read the user’s manual closely before using!,” Ecemedikal.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.ecemedikal.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/SX-1D-users-manual_eng.pdf. [Accessed: 07-Sep-2022].
[10]Skeet,Muriel and David Fear.“Electrical Suction Apparatus.” Care and Safe Use of Medical Equipment. VSO Books, 1995.
[11]Support, S., 2022. Suctioning. [online] Hopkinsmedicine.org. Available at: <https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/tracheostomy/living/suctioning.html> [Accessed 20 August 2022].
[12]Say, S., 2022. The Routine Maintenance You Should Be Performing on Your Suction Equipment. [online] Blog.sscor.com. Available at: <https://blog.sscor.com/the-routine-maintenance-you-should-be-performing-on-your-suction-equipment> [Accessed 25 August 2022].
[13]“800cc Disposable Suction Canister | Canisters | Suction Accessories | Suction Therapy | Respiratory | Products | Drive Medical US Site,” shop.drivemedical.com. https://shop.drivemedical.com/us/en/products/respiratory/suction-therapy/suction-accessories/canisters/800cc-disposable-suction-canister/p/367-1 (accessed Apr. 26, 2024).
[14]Laerdal Rechargeable Battery for LCSU4 Suction Units,” AED Superstore. [Online]. Available: https://www.aedsuperstore.com/laerdal-medical-rechargeable-battery-12vdc-nimh-lcsu4-suction-unit.html. [Accessed: 07-Sep-2022].
[15]“AboutKidsHealth,” Aboutkidshealth.ca. [Online]. Available: https://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/article?contentid=3852&language=english. [Accessed: 07-Sep-2022].